Telugu, one of India's most prominent languages, holds immense cultural and historical significance. It is not only the official language of Andhra Pradesh and Telangana but also a vital part of the Indian linguistic tapestry. With over 80 million native speakers worldwide, Telugu ranks as the third most spoken language in India and the fifteenth globally. This article delves into the language's origins, its impact on culture, and its modern relevance.
Telugu is not merely a means of communication; it is a reflection of the rich cultural heritage of the southern Indian states. From ancient inscriptions to modern literature, Telugu has played a pivotal role in shaping the identity of its speakers. As one of the classical languages of India, recognized by UNESCO, Telugu deserves a closer look into its history, evolution, and current status.
This comprehensive guide aims to provide an in-depth exploration of Telugu, covering its linguistic features, cultural significance, and contemporary applications. Whether you're a student of linguistics, a cultural enthusiast, or simply curious about this beautiful language, this article will offer valuable insights into the world of Telugu.
Read also:Ruth Aisling Husband A Comprehensive Guide To Her Life And Career
Table of Contents
- History and Origins of Telugu
- Classification and Linguistic Features
- The Telugu Script
- Telugu Literature: A Cultural Treasure
- Dialects and Regional Variations
- Telugu in Media and Entertainment
- The Role of Telugu in Education
- Global Presence of Telugu
- Efforts to Preserve and Promote Telugu
- The Future of Telugu
History and Origins of Telugu
The roots of Telugu trace back to the ancient Dravidian language family. Scholars believe that the language evolved from the Proto-Dravidian language spoken thousands of years ago. Early inscriptions in Telugu date back to the 5th century CE, showcasing its gradual development from a rudimentary script to a sophisticated linguistic system.
The earliest known Telugu inscription was discovered in the Erragudi region, providing valuable insights into the language's ancient form. Over centuries, Telugu absorbed influences from Sanskrit and other neighboring languages, enriching its vocabulary and grammatical structure.
Key Historical Milestones
- 5th Century CE: The first Telugu inscriptions appear.
- 11th Century CE: The "Andhra Mahabharata," an epic translation, marks the beginning of Telugu literature.
- 19th Century CE: Modernization of the language with the advent of printing technology.
Classification and Linguistic Features
Telugu belongs to the South-Central branch of the Dravidian language family. Its classification places it alongside other prominent Dravidian languages like Tamil and Kannada. Linguists admire Telugu for its systematic grammar, phonetic consistency, and rich vocabulary.
One of the distinguishing features of Telugu is its use of vowel harmony, where certain vowels in a word must align in terms of quality and length. This feature enhances the melody and rhythm of the language, making it aesthetically pleasing.
Unique Linguistic Traits
- Agglutinative nature: Words are formed by combining root words with affixes.
- Complex verb conjugations: Verbs change based on tense, mood, and subject-verb agreement.
- Rich phonetic inventory: Includes a wide range of consonants and vowels.
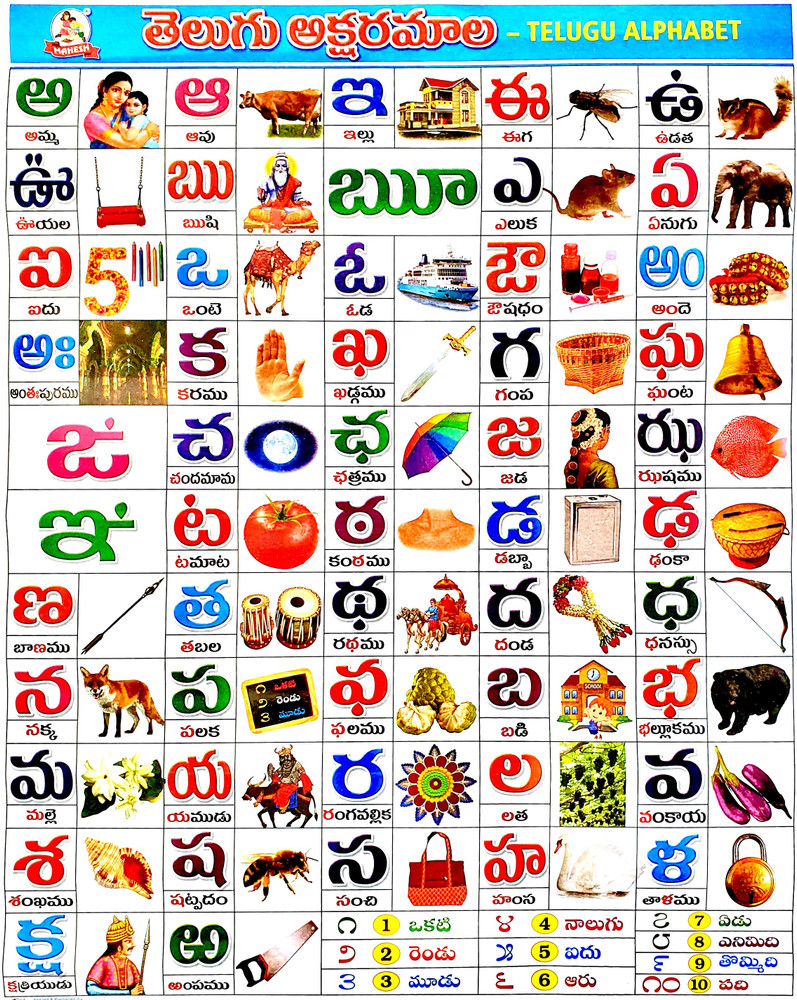
The Telugu Script
The Telugu script is an abugida, meaning each character represents a consonant-vowel combination. Developed from the ancient Brahmi script, it has undergone several modifications over the centuries. The script's rounded shapes and elegant curves reflect the artistic sensibilities of its creators.
Learning the Telugu script can be challenging for beginners due to its intricate characters and diacritical marks. However, its logical structure and systematic rules make it accessible with consistent practice.
Read also:Exploring The Cast Of I Now Pronounce You Chuck Amp Larry A Deep Dive Into The Comedy Classic
Components of the Telugu Script
- Consonants: 41 primary consonant letters.
- Vowels: 16 primary vowel symbols.
- Compound characters: Formed by combining consonants and vowels.
Telugu Literature: A Cultural Treasure
Telugu literature boasts a rich tradition spanning over a thousand years. From classical poetry to contemporary novels, the language has produced masterpieces that resonate with readers across generations. Prominent literary figures like Nannaya, Tikkana, and Yerrapragada have left an indelible mark on Telugu literary history.
Modern Telugu literature explores diverse themes, including social issues, philosophy, and human emotions. The works of Viswanatha Satyanarayana, a recipient of the Jnanpith Award, exemplify the depth and breadth of Telugu storytelling.
Notable Works in Telugu Literature
- "Andhra Mahabharata" by Nannaya, Tikkana, and Yerrapragada.
- "Kumara Sambhavam" by Bhattumurthy.
- "Ramayana Kalpavrikshamu" by Viswanatha Satyanarayana.
Dialects and Regional Variations
Telugu exhibits significant dialectal variations across different regions. These variations arise due to historical, geographical, and cultural factors. Some of the prominent dialects include:
Major Telugu Dialects
- Rayalaseema: Spoken in the southern part of Andhra Pradesh.
- Coastal Andhra: Characterized by its distinct intonation and vocabulary.
- Telangana: Reflects the influence of Urdu and Hindi.
Understanding these dialects enriches one's appreciation of the language's diversity and adaptability.
Telugu in Media and Entertainment
The Telugu film industry, often referred to as Tollywood, is one of the largest and most influential in India. Producing over 200 films annually, it caters to a vast audience both within India and abroad. Iconic actors like Akkineni Nageswara Rao and Chiranjeevi have contributed significantly to the popularity of Telugu cinema.
Television and digital media have further expanded the reach of Telugu content, making it accessible to a global audience. Streaming platforms now offer a wide range of Telugu shows and movies, ensuring the language's continued relevance in the digital age.
Impact of Telugu Media
- Boosts cultural pride among Telugu speakers.
- Provides employment opportunities in the entertainment sector.
- Promotes the language to non-native speakers.
The Role of Telugu in Education
Telugu plays a crucial role in the educational system of Andhra Pradesh and Telangana. It serves as the medium of instruction in schools and universities, ensuring that students receive a strong foundation in their native language. Efforts are ongoing to integrate Telugu into higher education and professional courses.
Language learning initiatives, both offline and online, aim to preserve and promote Telugu among younger generations. These programs emphasize the importance of bilingualism and cultural awareness in a globalized world.
Global Presence of Telugu
With a significant diaspora population, Telugu has gained prominence on the global stage. Communities in countries like the United States, Canada, and the United Kingdom actively preserve and promote the language through cultural events and educational programs.
Organizations such as the Telugu Association of North America (TANA) and the Telugu Society play pivotal roles in fostering a sense of belonging among Telugu speakers worldwide.
Global Telugu Initiatives
- Language workshops and cultural festivals.
- Collaborations with international universities for Telugu studies.
- Online platforms for learning and sharing Telugu content.
Efforts to Preserve and Promote Telugu
Preserving Telugu in the face of globalization requires concerted efforts from governments, educational institutions, and communities. Initiatives such as digitizing ancient manuscripts, promoting Telugu literature, and encouraging media consumption in the language are essential for its survival.
Technological advancements offer new avenues for language preservation. Mobile applications, online dictionaries, and digital archives make Telugu accessible to a broader audience, ensuring its relevance in the digital era.
The Future of Telugu
The future of Telugu looks promising, thanks to the dedication of its speakers and advocates. As younger generations embrace the language, its influence is likely to grow both within India and internationally. Continued efforts in education, media, and technology will play a vital role in shaping Telugu's future.
In conclusion, Telugu is more than just a language; it is a cultural cornerstone that deserves recognition and preservation. By understanding its history, appreciating its beauty, and supporting its growth, we can ensure that Telugu continues to thrive for generations to come.
Call to Action
We invite you to explore the world of Telugu further by reading related articles, engaging with the community, and sharing your thoughts in the comments section. Together, we can celebrate and preserve this magnificent language for the future.