New York income tax rate is a crucial aspect of financial planning for residents and businesses operating in the state. Understanding how the tax system works can significantly impact your financial health. Whether you're an individual taxpayer or a business owner, knowing the intricacies of New York's income tax structure is essential for maximizing your earnings and ensuring compliance with tax laws.
As one of the most populous and economically vibrant states in the United States, New York has a progressive income tax system that varies based on income levels. This article will delve into the details of New York's income tax rates, including how they are calculated, who is subject to them, and strategies for optimizing your tax obligations.
By the end of this guide, you'll have a clear understanding of New York income tax rates and how they affect your financial situation. Let's explore the topic in depth to ensure you're well-prepared for tax season and beyond.
Read also:Sone 436 A Comprehensive Guide To Understanding Its Significance
Table of Contents
- Introduction to New York Income Tax
- Current New York Income Tax Rates
- Understanding Filing Status
- Key Deductions and Credits
- New York Business Income Tax
- Using a Tax Calculator
- Federal vs. State Income Tax
- Impact of Tax Reforms
- Common Mistakes to Avoid
- Conclusion and Next Steps
Introduction to New York Income Tax
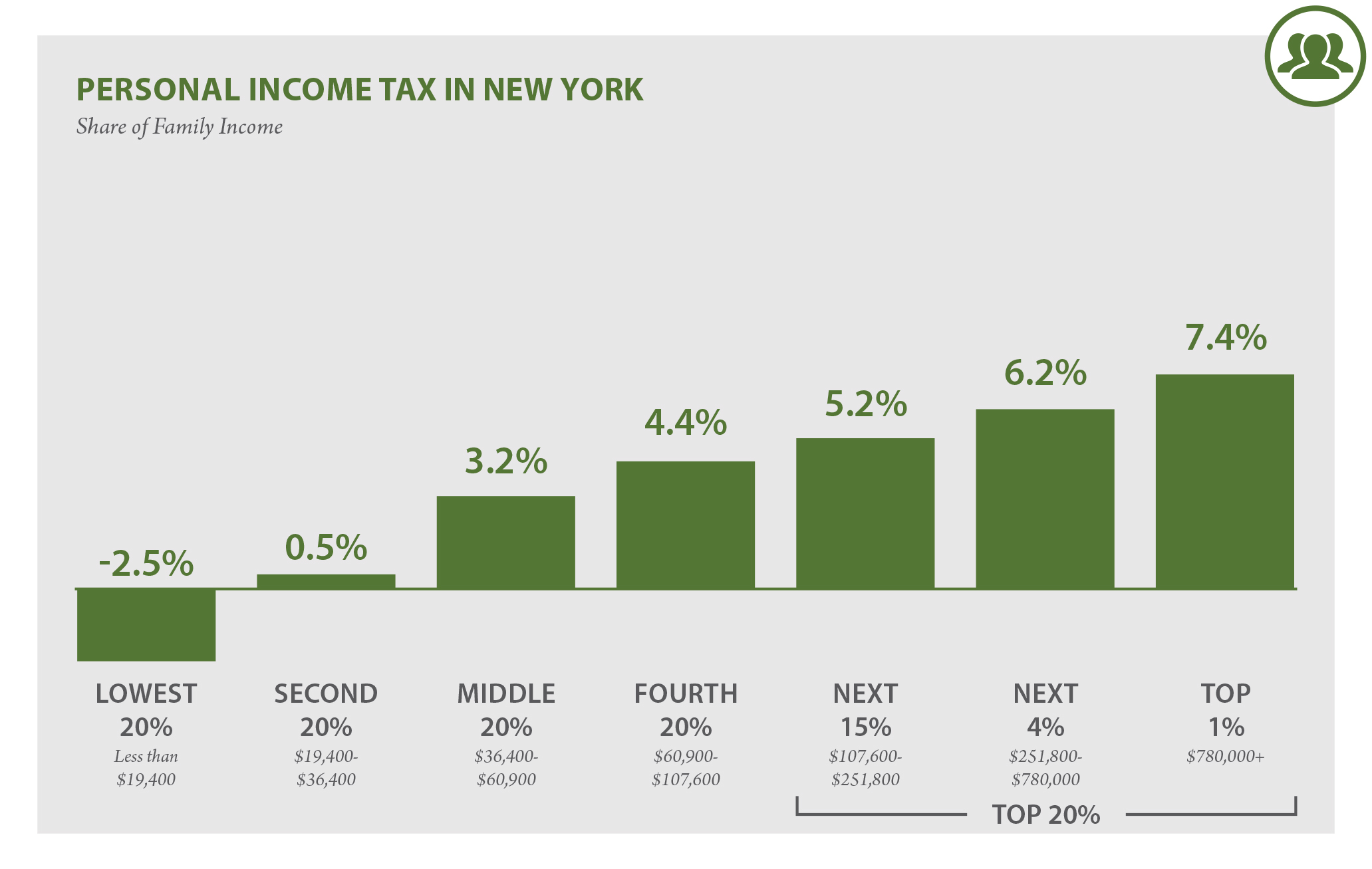
New York income tax is a critical component of the state's revenue system, funding essential services such as education, healthcare, and infrastructure. The tax rate is progressive, meaning higher income levels are taxed at higher rates. This system aims to ensure fairness in taxation by adjusting the burden based on an individual's ability to pay.
The state of New York imposes income tax on all residents, as well as non-residents who earn income within the state. The tax is calculated based on taxable income, which is determined after subtracting deductions and exemptions from gross income. Understanding the basics of New York income tax is the first step toward effective financial planning.
Who Pays New York Income Tax?
Both residents and non-residents are subject to New York income tax. Residents are taxed on their worldwide income, while non-residents are only taxed on income sourced from within the state. This distinction is important for individuals who work in multiple states or have international income sources.
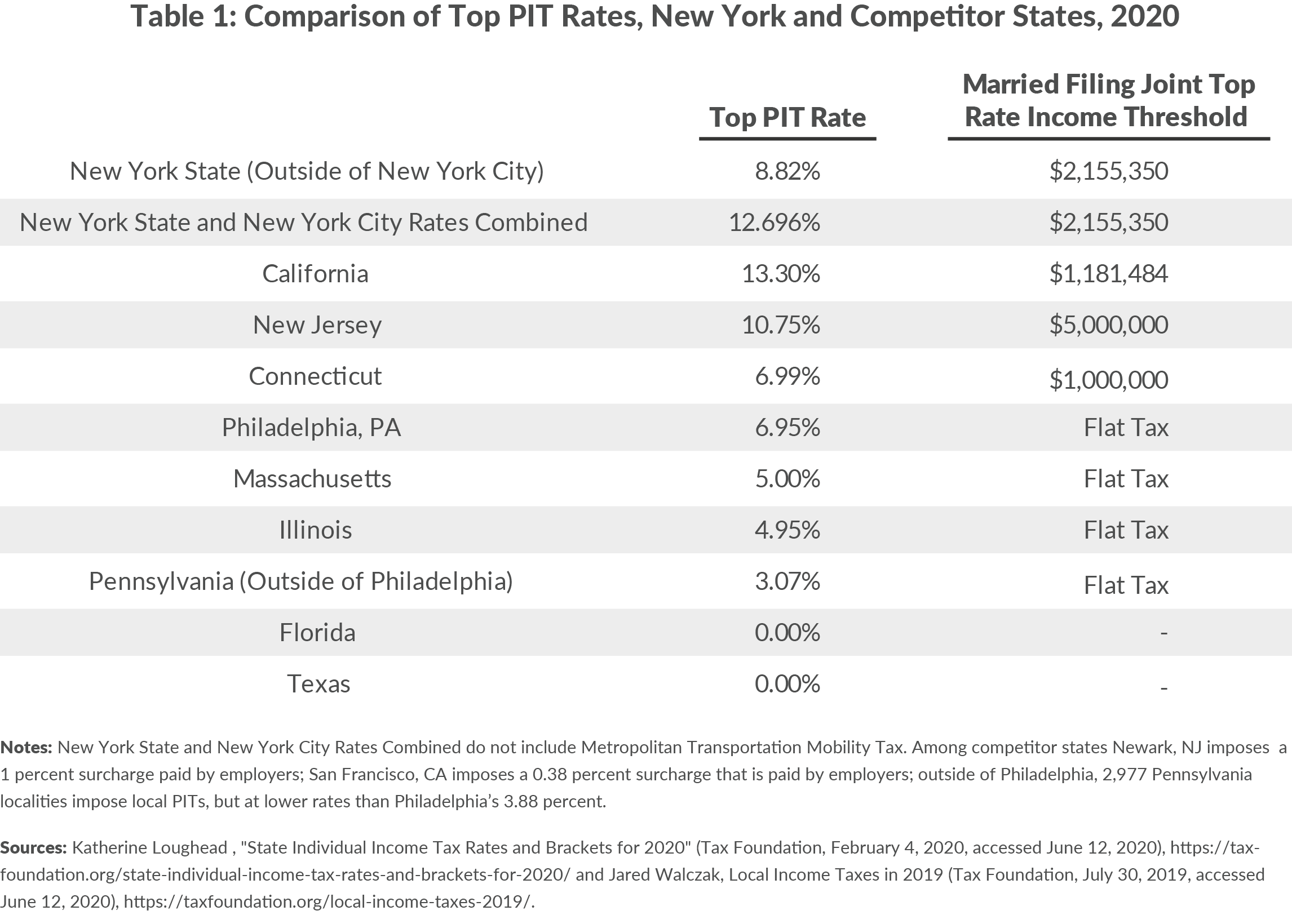
Current New York Income Tax Rates
As of the latest updates, New York employs a progressive tax system with several tax brackets. Each bracket corresponds to a specific income range and is taxed at a different rate. Below is an overview of the current tax rates:
- 4% for income up to $8,650
- 4.5% for income between $8,651 and $11,850
- 5.25% for income between $11,851 and $14,100
- 5.97% for income between $14,101 and $21,600
- 6.21% for income between $21,601 and $82,100
- 6.49% for income between $82,101 and $213,300
- 6.85% for income above $213,301
These rates are subject to change, so it's important to stay informed about any legislative updates that may affect your tax obligations.
Understanding Filing Status
Your filing status plays a significant role in determining your New York income tax rate. The state recognizes several filing statuses, including single, married filing jointly, married filing separately, and head of household. Each status has its own set of tax brackets and deductions, so selecting the correct status is crucial for accurate tax reporting.
Read also:Senator John Kennedy A Comprehensive Look At His Life Achievements And Impact
Choosing the Right Filing Status
To choose the appropriate filing status, consider your marital status, dependents, and household structure. For example, if you're married and filing jointly, you may benefit from lower tax rates and increased deductions compared to filing separately. Consulting with a tax professional can help ensure you make the best choice for your financial situation.
Key Deductions and Credits
One of the best ways to reduce your New York income tax liability is by taking advantage of available deductions and credits. These can significantly lower your taxable income, resulting in lower tax payments. Some of the most common deductions and credits include:
- Standard Deduction
- Itemized Deductions
- Child Tax Credit
- Earned Income Tax Credit (EITC)
- Education Credits
It's important to carefully review your eligibility for these deductions and credits to maximize your savings. Many taxpayers overlook valuable opportunities to reduce their tax burden by not fully understanding these options.
New York Business Income Tax
In addition to individual taxpayers, businesses operating in New York are also subject to income tax. The tax rate for corporations is a flat 6.5%, while pass-through entities such as partnerships and S corporations are taxed at the individual level. Understanding the tax implications for businesses is essential for effective financial management and compliance.
Tax Planning for Businesses
Businesses can employ various strategies to optimize their tax obligations, such as taking advantage of deductions for business expenses, investing in tax-advantaged retirement plans, and leveraging available credits. Consulting with a tax advisor familiar with New York's business tax laws can help ensure your business remains compliant and financially healthy.
Using a Tax Calculator
To simplify the process of calculating your New York income tax, many online tools and calculators are available. These tools allow you to input your income, deductions, and other relevant information to estimate your tax liability. While these calculators are convenient, they should not replace professional tax advice, especially for complex financial situations.
Benefits of Using a Tax Calculator
Using a tax calculator can help you:
- Estimate your tax liability quickly and accurately
- Identify potential deductions and credits
- Plan your finances more effectively
Federal vs. State Income Tax
While New York income tax is an important consideration, it's also crucial to understand how it interacts with federal income tax. Federal tax rates are also progressive, but they differ from state rates in terms of brackets and deductions. Coordinating your state and federal tax planning can lead to significant savings and improved financial outcomes.
Differences Between Federal and State Taxes
Key differences between federal and state income taxes include:
- Varied tax brackets and rates
- Different deduction and credit systems
- State-specific tax laws and regulations
Impact of Tax Reforms
Over the years, New York has undergone several tax reforms aimed at simplifying the tax code and improving fairness. These reforms have affected various aspects of the tax system, including rates, deductions, and credits. Staying informed about these changes is essential for maintaining compliance and optimizing your tax strategy.
Recent Tax Reforms in New York
Some of the recent tax reforms in New York include:
- Adjustments to tax brackets and rates
- Introduction of new credits and deductions
- Changes to filing deadlines and procedures
Common Mistakes to Avoid
When dealing with New York income tax, it's easy to make mistakes that can result in penalties or missed opportunities for savings. Some common mistakes include:
- Incorrectly reporting income or deductions
- Missing filing deadlines
- Overlooking available credits and deductions
To avoid these pitfalls, it's important to carefully review your tax documents and consult with a tax professional if needed.
Conclusion and Next Steps
In conclusion, understanding New York income tax rates and how they affect your financial situation is essential for effective tax planning. By familiarizing yourself with the current tax rates, deductions, and credits, you can optimize your tax obligations and improve your financial health. Remember to stay informed about any legislative changes that may impact your tax situation and consider consulting with a tax professional for personalized advice.
We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences in the comments section below. Additionally, feel free to explore other articles on our site for more insights into personal finance and tax planning. Together, let's take control of our financial futures!
Data Sources: