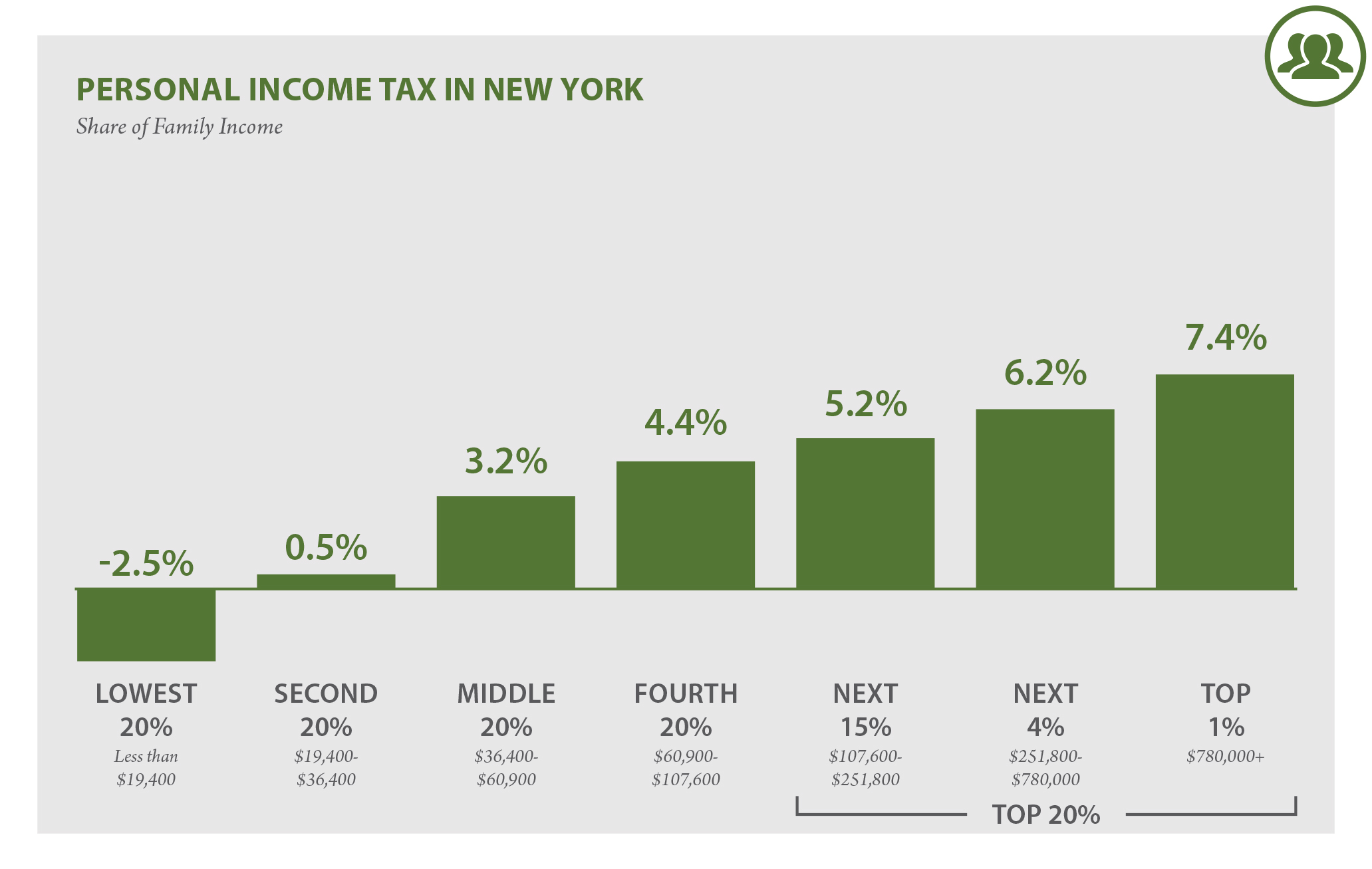
Understanding New York income tax rate is crucial for anyone living or earning income in the state. Whether you're a resident, small business owner, or simply curious about state tax obligations, this guide will provide everything you need to know. From the basics of income tax brackets to important deductions, exemptions, and filing tips, this article aims to simplify the complexities of New York's tax system.
Taxes are an integral part of our financial lives, and staying informed about state-specific tax laws can save you time, money, and stress during tax season. New York, known for its progressive tax structure, has a unique set of rules that affect residents and non-residents alike. This article will help demystify the complexities of New York's income tax system.
Whether you're preparing for tax season, planning your finances, or simply curious about how New York's tax rates compare to other states, this guide will serve as a valuable resource. Let's dive in!
Read also:How Old Is Megan Thee Stallion Everything You Need To Know About The Rising Star
Table of Contents
- Overview of New York Income Tax Rate
- Income Tax Brackets in New York
- Filing Status Options
- Deductions and Credits
- Tax Obligations for Non-Residents
- Penalties for Late Filing
- Useful Resources for Taxpayers
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Recent Updates and Changes
- Conclusion
Overview of New York Income Tax Rate
New York income tax rate operates on a progressive scale, meaning the tax rate increases as taxable income increases. This structure ensures that individuals with higher incomes contribute a larger percentage of their earnings to state revenue. The state's tax rates range from 4% to 10.9% depending on income level and filing status.
Key Features of New York's Tax System
New York's tax system includes several notable features:
- Progressive tax brackets tailored to individual income levels.
- Various deductions and credits designed to reduce taxable income.
- Different filing statuses to accommodate diverse taxpayer situations.
Data from the New York State Department of Taxation and Finance indicates that the majority of taxpayers fall into the lower tax brackets, benefiting from a more manageable tax burden.
Income Tax Brackets in New York
Understanding New York's income tax brackets is essential for estimating your tax liability. The state uses a progressive tax system, where higher income levels are taxed at higher rates. Below is a breakdown of the current tax brackets for the 2023 tax year:
Tax Brackets for Single Filers
For individuals filing as single:
- 4% on income up to $8,700
- 4.5% on income between $8,701 and $11,950
- 5.25% on income between $11,951 and $21,900
- 5.97% on income between $21,901 and $83,550
- 6.21% on income between $83,551 and $218,150
- 6.85% on income between $218,151 and $1,077,550
- 10.9% on income over $1,077,551
Tax Brackets for Married Couples Filing Jointly
For married couples filing jointly:
Read also:Best Guide To Downloading Mkvmoviespoint Web Series In Hindi
- 4% on income up to $17,400
- 4.5% on income between $17,401 and $23,900
- 5.25% on income between $23,901 and $43,800
- 5.97% on income between $43,801 and $167,100
- 6.21% on income between $167,101 and $436,300
- 6.85% on income between $436,301 and $2,155,100
- 10.9% on income over $2,155,101
These brackets are subject to change annually based on inflation adjustments and legislative updates.
Filing Status Options
Taxpayers in New York can choose from several filing statuses, each affecting their tax liability:
Single Filers
Individuals who are unmarried or legally separated at the end of the tax year and do not qualify for other statuses file as single.
Married Filing Jointly
Couples who file a single tax return together can benefit from higher income thresholds and potentially lower tax rates.
Married Filing Separately
Married couples who prefer to file separate returns may do so, but this option often results in higher taxes.
Head of Household
This status applies to unmarried individuals who maintain a home for a qualifying dependent, offering more favorable tax rates than single filers.
Choosing the correct filing status is crucial for optimizing your tax return and minimizing liability.
Deductions and Credits
New York offers a variety of deductions and credits to help taxpayers reduce their taxable income:
Standard Deduction
For the 2023 tax year, the standard deduction for single filers is $8,700, and for married couples filing jointly, it's $17,400.
Itemized Deductions
Taxpayers can choose to itemize deductions instead of taking the standard deduction. Common itemized deductions include:
- Mortgage interest
- Charitable contributions
- Medical expenses exceeding 7.5% of adjusted gross income
Tax Credits
Credits directly reduce the amount of tax owed. Some notable credits include:
- Child Tax Credit
- Earned Income Tax Credit (EITC)
- Education credits such as the Lifetime Learning Credit
Consulting a tax professional or using tax software can help ensure you claim all eligible deductions and credits.
Tax Obligations for Non-Residents
Non-residents who earn income in New York are also subject to state income tax. This includes individuals who work in New York but live elsewhere. The tax rate for non-residents is generally the same as for residents, but non-residents may not qualify for certain deductions and credits.
Key Points for Non-Residents
- Only income earned in New York is subject to state tax.
- Non-residents must file Form IT-203 to report their New York-source income.
- Certain exemptions apply for individuals with minimal New York income.
Understanding your obligations as a non-resident can prevent unexpected tax bills and penalties.
Penalties for Late Filing
Failing to file your New York state tax return by the deadline can result in significant penalties. The state imposes a late filing penalty of 5% of the unpaid tax for each month the return is late, up to a maximum of 25%. Additionally, there is a late payment penalty of 0.5% per month on any unpaid tax.
Avoiding Penalties
To avoid penalties, ensure you:
- File your return on time, even if you cannot pay the full amount due.
- Request an extension if you need more time to prepare your return.
- Pay any taxes owed by the deadline to avoid interest charges.
Staying organized and keeping track of deadlines is key to avoiding unnecessary fees.
Useful Resources for Taxpayers
Several resources are available to assist taxpayers in navigating New York's income tax system:
New York State Department of Taxation and Finance
The official website provides comprehensive information on tax laws, forms, and filing instructions.
Tax Preparation Software
Programs like TurboTax and H&R Block offer user-friendly interfaces for preparing and filing your taxes.
Professional Tax Advisors
Consulting a certified public accountant (CPA) or tax attorney can provide personalized guidance for complex tax situations.
Utilizing these resources can simplify the tax filing process and ensure compliance with state regulations.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What is the current top income tax rate in New York?
The highest income tax rate in New York is 10.9%, applicable to income over $1,077,551 for single filers and $2,155,101 for married couples filing jointly.
2. Are there any special tax breaks for low-income taxpayers?
Yes, New York offers the Earned Income Tax Credit (EITC) to help low- to moderate-income taxpayers reduce their tax liability.
3. Can I file my New York state tax return online?
Yes, you can file your New York state tax return electronically through the Department of Taxation and Finance's website or authorized tax preparation software.
Recent Updates and Changes
Stay informed about recent updates to New York's tax laws:
2023 Tax Law Changes
In 2023, New York introduced several changes, including:
- Increased standard deduction amounts to account for inflation.
- Expanded eligibility for certain tax credits.
- Updated filing deadlines due to federal legislation.
Regularly checking for updates ensures you remain compliant with the latest tax regulations.
Conclusion
Understanding New York income tax rate is essential for managing your financial obligations effectively. By familiarizing yourself with tax brackets, filing statuses, deductions, and credits, you can minimize your tax liability and maximize your refund. Remember to stay informed about updates to tax laws and utilize available resources to make the filing process smoother.
We encourage you to share this article with others who may benefit from the information. If you have questions or need further clarification, feel free to leave a comment below. Additionally, explore our other articles for more insights into personal finance and tax planning.